Pivotal/Cloud Foundry
From r00tedvw.com wiki
Cloud Foundry | Cloud Foundry CLI | Apps | Tasks
Contents[hide] |
Overview
Software Platform that lets you build and run software in a consistent way, in any place.
Runs across any platform such as:
- Amazon Web Services
- Microsoft Azure
- Google Cloud Platform
- Open Stack
- VMWare
Cloud Foundry builds out the infrastructure including the virtual machine and a hardened version of the operating system, Windows or Linux.
Hierarchy
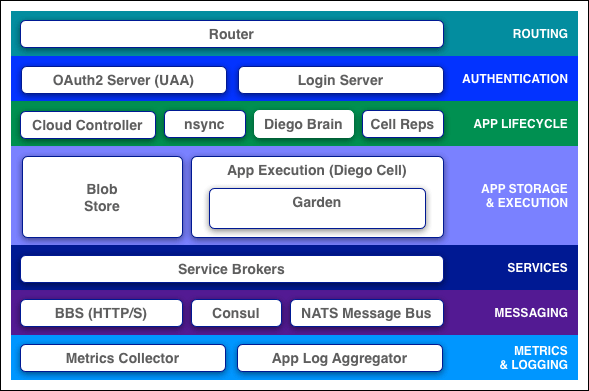
Fundamental Concepts
Process Changes
- Distributed System
- Distributed systems are hard to build, test, manage, and scale.
- Ephemeral Infrastructure
- Virtual machines and containers are temporary
- Immutable Infrastructure
- Updates to systems and applications are not done in-place but rather new, updated instances are created instead.
Elastic Runtime (CF)
Diego
Schedules tasks and long-running processes (LRPs)
- Task - guaranteed to run at most once
eg. stage and application - LRP - a long running process, typically represented as a web app. lrps can have multiple instances.
- Container - An application instance is run within an immutable container
- Cell - Containers are run within a cell.
- Garden - Containers are managed by Garden.
- Rep - represents the cell in the BBS/auctions
- Auction - auctions are held to bid on executing a task or an LRP.
- Executor - Manages container allocations on the cell. Also streams
stdoutandstderrto Metron - Metron - Forwards logs to the loggregator subsystem
- BBS - Bulletin Board System is the API to access the Diego database for tasks and LRPs.
- Brain - The brain is composed of two components, the auctioneer which holds auctions for tasks and LRPs, and the Converger which reconciles desired LRPs vs Actual LRPs through auctions.
Loggregator
- Metron - Forwards logs to the loggregator subsystem
- Doppler - Gathers logs from Metron. also has app syslog drains to services like splunk or papertrail.
- Traffic Controller - Handles client requests for logs. Also exposes a web socket endpoint called the firehose.
- Firehose - A websocket endpoint that exposes app logs, container metrics, and ER component metrics.
- Nozzles - Consume the firehose output
Cloud Controller API
The Cloud Controller exposes an API for using and managing the Elastic Runtime (CF)
- Cloud Controller Database - The cloud controller persists org/space/app data in the cloud controller database
- Blob Store - The cloud controller persists app packages and droplets to the blob store.
- CC-Bridge - The CC-Bridge translates app specific messages into the generic language of tasks and LRPs.
Routing
The router routes traffic to appropriate components and all app instances.
The router round robins between application instances